背景介绍
转染使我们能够更好地理解目标基因在细胞中是如何表达和调节的。目前常见的转染方法包括磷酸钙共沉淀、电穿孔、DEAE-葡聚糖和聚脲嘧啶、机械方法(如显微注射和基因枪)以及阳离子脂质体转染试剂,其中阳离子脂质体转染试剂是常用的一种。
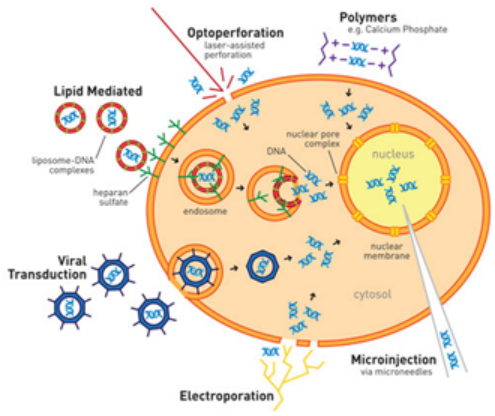
Figure 1: Schematic Diagram of Different Transfection Methods (Image source: Daily Biology Reviews)
不同转染方法比较
|
Transfection Method |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Calcium Phosphate Co-precipitation |
Low cost, relatively simple operation |
Unstable transfection efficiency, prone to issues such as DNA aggregation affecting transfection efficiency, high cytotoxicity, poor transfection efficiency |
|
Electroporation |
High efficiency, suitable for all types of cells |
Expensive electroporation equipment, high cell death rate, requires large amounts of nucleic acids and cells |
|
DEAE-Dextran |
Effective for transfection of adherent cells, can also be used for certain suspension cells, simple operation, repeatable results |
Cell preference, some toxicity to cells, serum inhibition of cell growth required during transfection |
|
Polybrene |
Relatively simple operation, moderate price |
Low efficiency, some limitations in application |
|
Cationic Lipid Reagents |
Simple operation, high efficiency, wide applicability, good repeatability, low toxicity |
Slightly higher price compared to other chemical reagents |
|
Viral Transduction |
High efficiency, effective for difficult-to-transfect cells, good transduction in primary cells |
Complex viral packaging process, some risk associated with viruses |
|
Polyethylenimine (PEI) |
Low price, simple operation, wide applicability |
Lower efficiency compared to lipid-based transfection reagents, some cells exhibit sensitive reactions after contact |
已验证细胞系
Celthy Trans脂质体核酸转染试剂作为一种阳离子脂质体转染试剂,与广泛使用的Lipo2000相比,具有更高的转染效率和更便捷的操作性。它已在多种细胞系中得到验证,如下是经过验证的细胞系列表。
|
A549 |
BV-2 |
BV50 |
C2C12 |
Calu 1 |
CHO |
Caco2 |
|
C6 |
COS-7 |
DF-1 |
H299 |
H520 |
HaCaT |
HCT116 |
|
HEK293 |
HEK 293T |
HeLa |
Hep2C |
Hep3B |
Hepa1-6 |
HepG2 |
|
HK2 |
HO1980 |
HUVEC |
HaCaT |
HUVEC |
H520 |
H9C2 |
|
H9 |
LM3 |
Lenti X-293T |
MCF10A |
MCF-7 |
MDA-MB-231 |
MDCK |
|
MEF |
MKN-28 |
N2A |
NCI-H1975 |
NIH-3T3 |
Neuro-2a |
PC12 |
|
Raw264.7 |
RKO |
SGC-7901 |
SMCC7721 |
T47D |
THP-1 |
TS |
|
U-87 |
Vero |
WEHI |
WRL-68 |
3t3 |
5-8F |
93T |
|
293FT |
多发性骨髓瘤细胞 |
More… |
|
|
|
|
作用机理
阳离子脂质体可以通过其表面的正电荷与核酸的负电荷通过静电相互作用包裹核酸,形成核酸-脂质体复合物。细胞膜表面带有负电荷,使得复合物能够被吸附。一旦被吸附,复合物可以通过膜融合或内吞作用进入细胞,形成细胞内的包含体。一小部分DNA可以从包含体中释放出来,进入细胞质,进一步进入细胞核进行转录和表达。
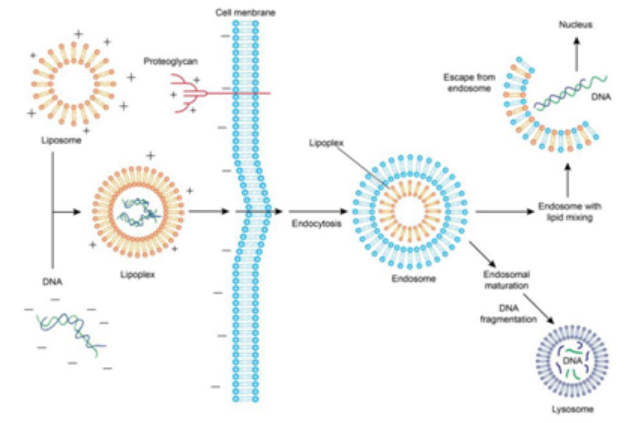
Figure 2: Liposome-mediated Transfection and Endocytosis Process
转染试剂产品特点:
高效率:能够转染大多数真核细胞,对常见细胞系的转染效率超过90%;
低毒性:转染的细胞形态良好,能高水平表达转染的基因蛋白;
操作便捷:脂质体复合物可以直接添加到含有血清的培养基中;
多用途:适用于瞬时和稳定转染实验。
操作流程
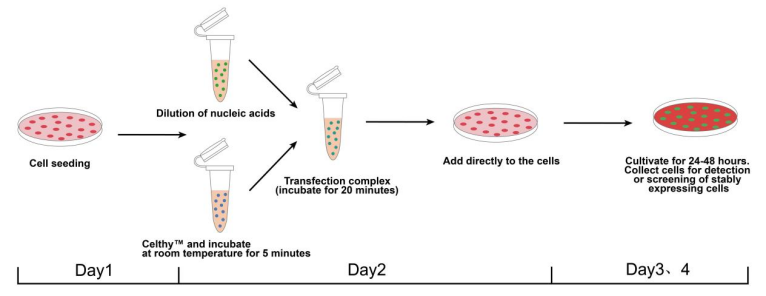
Figure 3: Cell Transfection Experimental Workflow
产品数据
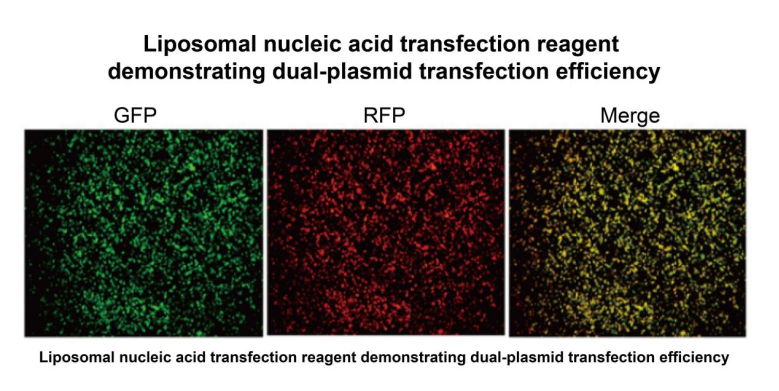
Figure 4: Dual Plasmid Transfection Reagent Validation Results
客户反馈数据
Celthy Trans Liposomal Transfection Application
|
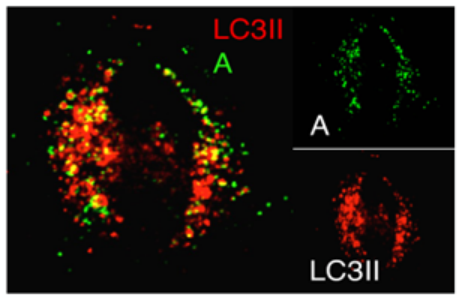
Activation of Cell Autophagosome Formation by Bacterial Protein Cell: HeLa Transfected Plasmid: Bacterial Effector Protein A LC3II: Autophagosome Marker Protein |
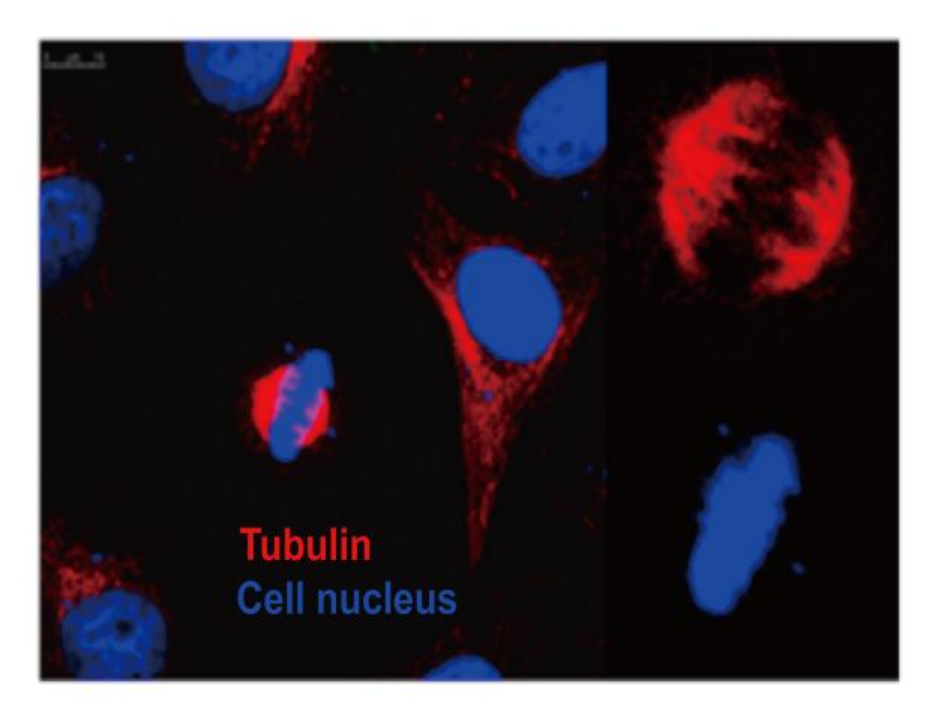
Hoechst 33342 Spindle Structure during Cell Division Cell: HeLa Transfected Plasmid: Flag-tubulin Nuclear Staining: Hoechst 33342 |
||
|
Celthy Trans |
Lipo3000 |
Celthy Trans |
Lipo2000 |
|
Image Source: Fudan University Cell Line: HEK293 Nucleic Acid Type: DNA |
Image Source: Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry Cell Line: HeLa Nucleic Acid Type: DNA |
||
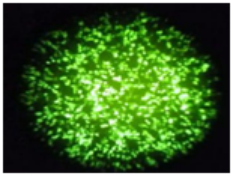
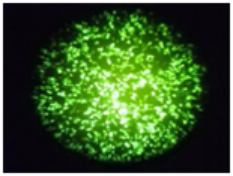
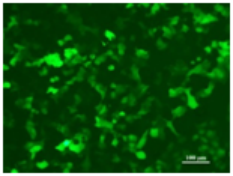
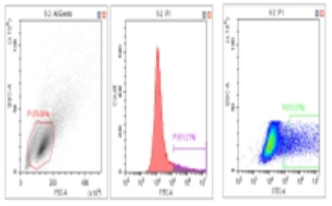
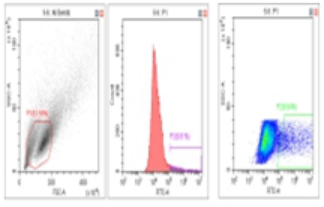
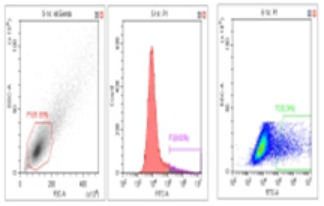
Flow Cytometry Fluorescence Observation Results
|
Celthy Trans (13.27%) |
Lipo2000 (8.64%) |
FuGenHD (9.24%) |
|
Cell Line: C2C12 Fluorescent Protein: EGFP (Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein) Nucleic Acid Type: DNA Data Source: South China Agricultural University |
||
客户提供的部分细胞转染数据(仅供参考)
|
Cell |
Culture Plate |
Cell Density |
DNA |
Celthy Trans |
Efficiency |
|
293T |
6 well |
80% |
1μg |
2μL |
90% |
|
293FT |
24 well |
85% |
1μg |
4μL |
90% |
|
Hela |
12 well |
90% |
0.2μg |
0.6μL |
90% |
|
Raw264.7 |
35mm plate |
80% |
1μg |
2μL |
90% |
|
Hek293 |
6 well |
95% |
2μg |
10μL |
80-90% |
|
NCI-H1975 |
6 well |
80% |
4μg |
10μL |
80% |
|
3t3 |
12 well |
90% |
1μg |
5μL |
50% |
常见问题
Q1: 准备核酸转染试剂复合物时可以有血清存在吗?
a: 血清的存在可能会影响脂质体的形成。建议在准备核酸转染试剂复合物时使用无血清培养基(通常为MEM培养基)。
Q2: 在转染实验中需要更换为无血清培养基吗?
a: 不需要,我们的转染试剂可以在含有血清的培养基中进行转染。
Q3: 转染后需要终止转染吗?
a: 不需要。脂质体复合物可以稳定存在6小时。如果转染前没有更换细胞培养基,需要在转染后4-6小时更换为新鲜培养基,以确保细胞正常生长所需的营养物质。但如果转染前已经更换了培养基,则在脂质体转染后不需要再次更换培养基。
Q4: 存储和使用转染试剂时需要注意什么?
a: 该试剂必须存放在4°C。避免反复长时间开盖,因为长时间暴露在空气中可能会导致脂质体氧化,影响转染效率。
Q5: 如何提高转染效率?
a: 转染时的细胞密度,保持在90%-95%。
b: 转染过程中使用MEM无血清培养基稀释核酸和脂质体稀释液。
c: 转染后4-6小时可以更换培养基。
产品推荐
|
Product Name |
Catalog number |
Specification |
|
C130002S |
0.5 mL |
|
|
C130002M |
1.0 mL |
产品试用:扫描二维码,即刻申请